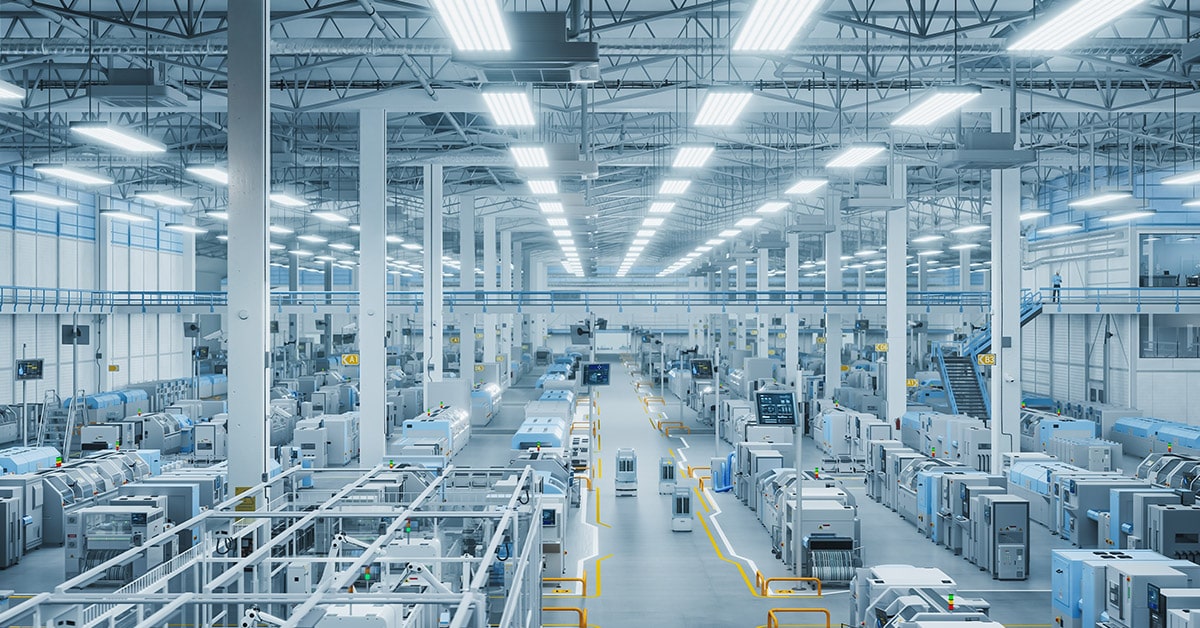
The world of industrial architecture is evolving rapidly, influenced by technological advancements, sustainability goals, and automation-driven efficiency. Manufacturing facilities are no longer just large warehouses with production lines—they are becoming smart, sustainable, and highly adaptable to industry demands. With the rise of Industry 4.0, green building initiatives, and flexible modular designs, architects are rethinking how manufacturing spaces function in the modern age.
As industries embrace digital transformation, the role of architectural innovation becomes critical in shaping future-ready manufacturing facilities. This article explores the latest trends in industrial architecture and how they are redefining the future of manufacturing.
1. Smart Factories and Industry 4.0 Integration
The Shift Toward Digital Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing manufacturing by integrating AI, IoT (Internet of Things), robotics, and cloud computing into factory operations. Industrial architecture must accommodate smart technologies while ensuring efficiency and safety.
Key Design Adaptations for Smart Factories:
- AI-Optimized Layouts: Factories are designed with automated production lines, robotic arms, and real-time monitoring systems.
- IoT-Connected Infrastructure: Sensors track machine performance, energy use, and environmental conditions for predictive maintenance.
- Automated Material Handling: AI-powered conveyor systems and self-navigating AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) improve logistics.
- Data-Driven Facility Management: Smart buildings use real-time data analytics to optimize energy consumption and resource allocation.
As Industry 4.0 continues to expand, industrial buildings must be designed for high-tech manufacturing environments.
2. Sustainable and Green Manufacturing Facilities
The Push for Eco-Friendly Industrial Design
Sustainability is at the core of modern industrial architecture. Manufacturing plants are major energy consumers, and companies are prioritizing low-carbon building materials, renewable energy, and efficient resource management.
Green Industrial Architecture Trends:
- Solar-Powered Factories: Rooftop solar panels and wind turbines are reducing energy costs and carbon emissions.
- Green Roofs and Natural Insulation: Plants with vegetation-covered roofs and energy-efficient insulation improve indoor temperature control.
- Water Recycling Systems: Manufacturing plants are incorporating greywater reuse and rainwater harvesting for cooling and sanitation.
- Eco-Friendly Construction Materials: Use of recycled steel, low-carbon concrete, and sustainable wood alternatives.
As businesses align with global sustainability goals, architects focus on creating environmentally responsible manufacturing facilities.
3. Modular and Flexible Factory Designs
Why Flexibility Matters in Industrial Architecture
With shifting market demands and rapid technological advancements, manufacturing facilities must be adaptable to new production needs. Modular designs allow factories to expand or reconfigure without major renovations.
Key Features of Modular Manufacturing Facilities:
- Pre-Fabricated Building Components: Modular walls, expandable production areas, and movable workstations allow factories to scale operations efficiently.
- Multi-Use Spaces: Facilities are designed to accommodate multiple production lines within the same footprint.
- Quick Adaptation for New Technologies: Flexible layouts allow manufacturers to incorporate new automation and robotics without disrupting workflows.
These adaptable designs help companies remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
4. Advanced Safety and Worker-Centric Designs
Prioritizing Safety and Employee Well-Being
Modern manufacturing facilities must be safe, ergonomic, and designed for workforce efficiency. Architects focus on worker-centric designs that improve productivity and reduce health risks.
Safety Enhancements in Industrial Architecture:
- Noise-Reducing Materials: Soundproofing solutions protect workers from machinery-related hearing damage.
- Optimized Lighting Systems: LED smart lighting reduces eye strain and improves visibility in production areas.
- Ventilation and Air Quality Controls: HEPA-filtered air systems and natural ventilation reduce exposure to dust, fumes, and airborne contaminants.
- Emergency Response Design: Facilities incorporate wide evacuation routes, fire-resistant materials, and automated hazard detection systems.
By enhancing safety through architectural design, factories ensure higher productivity and worker satisfaction.
5. Vertical Manufacturing and Space Optimization
Maximizing Space Efficiency in Industrial Facilities
With rising land costs, manufacturers are turning to vertical industrial spaces to optimize limited real estate.
Vertical Factory Trends:
- Multi-Level Manufacturing Floors: Factories are being designed with stacked production areas to reduce land use.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Robotic storage solutions maximize space utilization.
- Underground and Rooftop Production Zones: Some facilities integrate subsurface production areas or rooftop assembly lines.
Vertical factories allow manufacturers to operate efficiently in urban and high-density areas.
6. Resilient and Disaster-Resistant Industrial Architecture
Building Factories for Extreme Conditions
Manufacturing plants must be designed to withstand natural disasters, power failures, and supply chain disruptions.
Resilient Factory Design Elements:
- Seismic-Resistant Structures: Shock-absorbing foundations and reinforced steel framing prevent earthquake damage.
- Flood Protection and Storm-Ready Designs: Elevated structures, waterproof materials, and advanced drainage systems mitigate disaster risks.
- Redundant Power Supply Systems: Backup generators, off-grid solar panels, and battery storage solutions ensure continuous operations.
These features protect industrial investments and ensure long-term operational stability.
7. The Rise of High-Tech Data-Driven Factories
Integrating AI and Digital Twins in Manufacturing
Modern industrial facilities use AI and digital twins to simulate, optimize, and improve production processes before physical implementation.
Digital Factory Innovations:
- 3D-Modeled Smart Factories: Digital twins replicate factory layouts in virtual environments to test efficiencies before construction.
- AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning predicts maintenance needs, production bottlenecks, and energy consumption patterns.
- Automated Quality Control Systems: AI-powered inspection stations reduce defects and improve product consistency.
These high-tech solutions boost productivity, minimize errors, and enhance real-time decision-making.
Conclusion
The future of industrial architecture is driven by smart technology, sustainability, modular flexibility, and worker safety. As manufacturing evolves, architects must integrate energy-efficient solutions, automation-ready designs, and disaster-resistant structures to create next-generation industrial facilities.
Leading firms like Stendel + Reich architects specialize in designing high-performance, adaptable, and future-ready manufacturing plants that meet industry demands while prioritizing efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
With innovations in vertical factories, AI-driven automation, and sustainable materials, the industrial spaces of tomorrow will be more efficient, technologically advanced, and environmentally responsible than ever before.