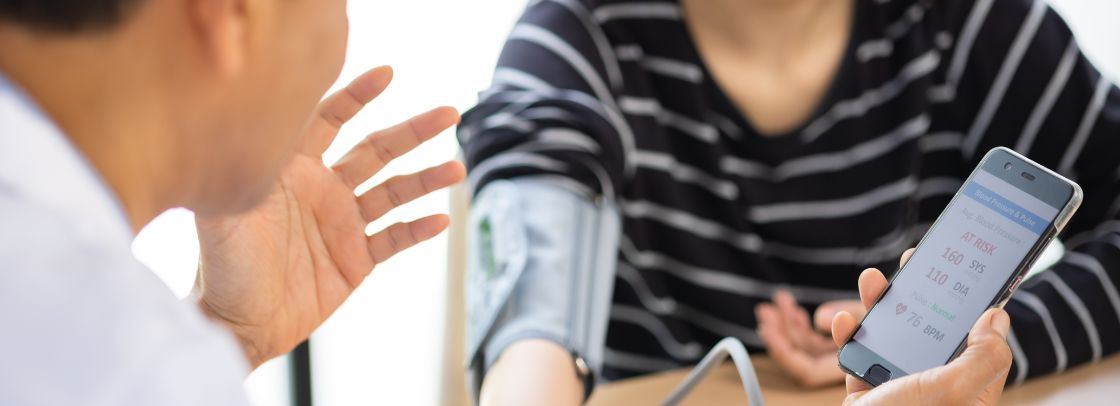
Hypertension, often referred to as high blood pressure, is a health condition that is typically associated with older adults. However, there is a growing concern about the increasing prevalence of hypertension in young adults. This condition, if left unmanaged, can lead to severe health complications. In this article, we will explore the various factors that can cause hypertension in young adults.
Poor Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in overall health, including blood pressure regulation. Young adults who consume a diet high in sodium, processed foods, and sugary beverages are at an increased risk of developing hypertension. Excess sodium intake can lead to water retention and increased blood volume, raising blood pressure levels. It is essential to maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support cardiovascular health.
Lack of Physical Activity
A sedentary lifestyle is a significant contributor to hypertension in young adults. Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and decreased cardiovascular fitness, both of which are risk factors for high blood pressure. Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps control weight but also strengthens the heart and improves blood vessel health, reducing the risk of hypertension.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Tobacco and excessive alcohol use are risk factors for hypertension. Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of plaque buildup, which can narrow arteries and raise blood pressure. Excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to hypertension. Consider monitoring your alcohol intake using tools like Soberlink if you’re concerned about its impact on your blood pressure. Soberlink Reviews share the experience of many people recovering from alcoholism successfully.
Obesity
Obesity is a well-established risk factor for hypertension. Young adults who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop high blood pressure. Excess body fat can increase the workload on the heart and lead to insulin resistance, which can contribute to hypertension. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial in preventing and managing hypertension.
Genetics and Family History
Hypertension can have a genetic component, meaning that if you have a family history of high blood pressure, you may be at an increased risk. It’s important for young adults to be aware of their family’s health history and take proactive measures to monitor and manage their blood pressure regularly. Genetic predisposition, combined with lifestyle factors, can significantly impact the development of hypertension.
Stress
Chronic stress and anxiety can contribute to hypertension in young adults. Stress triggers the release of hormones that can temporarily raise blood pressure. Over time, frequent or prolonged stress can lead to sustained high blood pressure levels. Learning stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can be beneficial in preventing hypertension.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. It is associated with hypertension, especially in young adults. The repeated episodes of interrupted breathing can lead to increased blood pressure during the night and, over time, result in sustained high blood pressure levels. Treating sleep apnea with lifestyle changes or medical interventions can help manage blood pressure.
Hypertension is not just a concern for older individuals; it can affect young adults as well. Understanding the various factors that contribute to high blood pressure in this demographic is crucial for prevention and early intervention. By adopting a healthy diet, staying physically active, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and addressing sleep apnea if necessary, young adults can reduce their risk of hypertension and promote long-term cardiovascular health. If you have concerns about alcohol consumption’s impact on your blood pressure, consider using tools like Soberlink reviews to monitor and manage your alcohol intake effectively. Regular monitoring and a proactive approach to heart health are key to preventing hypertension and its associated complications.